
Lactoeye® With Brainberry®
RM153.00 – RM918.00
Bioactive Collagen Peptides™(Germany)
Bioactive Collagen Peptides™(Germany)
Bioactive Collagen Peptides™ (BCP) are derived from enzymatically hydrolyzed collagen, containing key amino acids—glycine, proline, and hydroxyproline. BCP is quickly absorbed into the cartilage, promoting cartilage regeneration via the anabolic pathway. It stimulates the production of Type II collagen and glycosaminoglycans (GAG) to protect against cartilage wear and tear.
Lactoeye® With Brainberry®
RM153.00 – RM918.00
See clearer, think sharper, and stay stronger! LACTOEYE® with BRAINBERRY® blends powerful ingredients to support your vision, enhance mental clarity, boost immunity, and promote gut health. Ready-to-consume and perfect for all ages especially your little ones.
Consumption Guide:
Child (age 4 and above): 1 sachet after meal
Adult: 1-2 sachets after meal

Empowering Eye-Brain Fitness, Immunity & Gut Health
Beyond clear vision, LACTOEYE® with BRAINBERRY® strengthens the eye-brain connection, enhancing focus, learning, and quick thinking to keep you sharp every day. With improved immunity and gut balance, you'll feel more energized, empowered, and ready to take on anything! And taste-wise? An irresistible berry punch that melts in your mouth.
Provides powerful antioxidants that reduce eye dryness and fatigue, improve retinal health, and protect against oxidative damage.
Rich in lutein and zeaxanthin, which filter blue light, protect the retina, and improve visual sharpness and macular health, supporting long-term eye protection.
Enhances brain function by increasing neural signaling, improving eye-hand coordination, focus, and memory retention, perfect for mental sharpness and performance.
Strengthen immune defenses, providing antioxidant protection and supporting gut health, essential for immunity and overall wellness.
Promotes digestive health by balancing gut bacteria and effectively reducing stress induced gastrointestinal symptoms.

The Patented Ingredients
Bilberon®
-25 Bilberry Extract
BILBERON®-25 is a highly concentrated bilberry extract made from fresh fruits in northern Europe and standardized to contain at least 25% anthocyanidins by Tokiwa Phytochemicals Japan. Clinically proven to enhance visual performance, maintain healthy blood vessels, and hydrate the eyes, BILBERON®-25 also promotes the re-composition of rhodopsin and provides potent antioxidant properties for optimal eye health. In just under 2 months, BILBERON®-25 has been shown to significantly improve eye dryness and fatigue.
XanMax®
Marigold Flower Extract
XanMax® is a patented US extract from Marigold flowers, standardized to highly bioavailable free-form Lutein and Zeaxanthin, the primary yellow to red pigment macular carotenoids in the retina and lens. Acting as antioxidants and blue light filters, they improve visual performance, as shown in a meta-analysis of eight randomized control trials. Lutein and Zeaxanthin also increase macular pigment optical density (MPOD) by 40% in 180 days, improve visual acuity and memory in 12 months, and buffer against age-related declines in verbal learning and memory.
Brainberry
Aronia Berry Extract
Aronia berry (Aronia Melanocarpa), also known as black chokeberry, is a superfruit that contains high levels of polyphenols and antioxidants. These properties have been proven to improve the immune system and brain fitness of all ages.
BRAINBERRY® is a patented Aronia berry Extract produced by BioActor BV (Netherlands), standardized to contain a high concentration of anthocyanin ( > 15% cyanidin-3-galactosides). Proven by clinical studies, this nootropic nutraceutical has the capacity to improve cognitive health and memory.
Micro-Encapsulated Probiotics
(10 Billion CFU)
LACTOEYE® with BRAINBERRY® utilizes a high-performance micro-encapsulated probiotics Bifidobacterium longum Rosell®-175, that are highly stable and resistant to gastric acidity, compression and heat shock. This probiotic has been associated with numerous health benefits, such as normalising gastrointestinal transit, inhibiting the growth of harmful bacteria, boosting the immune system, and effectively reducing stress induced gastrointestinal symptoms. This probiotic has also been shown to improve gut and cognitive health via the gut-brain axis., enhancing mood and reducing stress related symptoms.
Liposomal Vitamin C
Liposomal Vitamin C is encapsulated in a lipid bilayer, allowing 233% greater absorption and retention than standard Vitamin C. This form offers superior antioxidant protection, helps defend the lens against UV damage, reduces cataract risk, and boosts immune function, with studies indicating enhanced neuron growth, immune support, and ocular health benefits.
The Patented Ingredients
Bilberon®-25 Bilberry Extract
BILBERON®-25 is a highly concentrated bilberry extract made from fresh fruits in northern Europe and standardized to contain at least 25% anthocyanidins by Tokiwa Phytochemicals Japan. Clinically proven to enhance visual performance, maintain healthy blood vessels, and hydrate the eyes, BILBERON®-25 also promotes the re-composition of rhodopsin and provides potent antioxidant properties for optimal eye health. In just under 2 months, BILBERON®-25 has been shown to significantly improve eye dryness and fatigue.
XanMax® Marigold Flower Extract
XanMax® is a patented US extract from Marigold flowers, standardized to highly bioavailable free-form Lutein and Zeaxanthin, the primary yellow to red pigment macular carotenoids in the retina and lens. Acting as antioxidants and blue light filters, they improve visual performance, as shown in a meta-analysis of eight randomized control trials. Lutein and Zeaxanthin also increase macular pigment optical density (MPOD) by 40% in 180 days, improve visual acuity and memory in 12 months, and buffer against age-related declines in verbal learning and memory.
Brainberry® Aronia Berry Extract
Aronia berry (Aronia Melanocarpa), also known as black chokeberry, is a superfruit that contains high levels of polyphenols and antioxidants. These properties have been proven to improve the immune system and brain fitness of all ages.
BRAINBERRY® is a patented Aronia berry Extract produced by BioActor BV (Netherlands), standardized to contain a high concentration of anthocyanin ( > 15% cyanidin-3-galactosides). Proven by clinical studies, this nootropic nutraceutical has the capacity to improve cognitive health and memory.
Brainberry® Aronia Berry Extract
Aronia berry (Aronia Melanocarpa), also known as black chokeberry, is a superfruit that contains high levels of polyphenols and antioxidants. These properties have been proven to improve the immune system and brain fitness of all ages.
BRAINBERRY® is a patented Aronia berry Extract produced by BioActor BV (Netherlands), standardized to contain a high concentration of anthocyanin ( > 15% cyanidin-3-galactosides). Proven by clinical studies, this nootropic nutraceutical has the capacity to improve cognitive health and memory.
Micro-Encapsulated Probiotics
(10 Billion CFU)
LACTOEYE® with BRAINBERRY® utilizes a high-performance micro-encapsulated probiotics Bifidobacterium longum Rosell®-175, that are highly stable and resistant to gastric acidity, compression and heat shock. This probiotic has been associated with numerous health benefits, such as normalising gastrointestinal transit, inhibiting the growth of harmful bacteria, boosting the immune system, and effectively reducing stress induced gastrointestinal symptoms. This probiotic has also been shown to improve gut and cognitive health via the gut-brain axis., enhancing mood and reducing stress related symptoms.
Micro-Encapsulated Probiotics
(10 Billion CFU)
LACTOEYE® with BRAINBERRY® utilizes a high-performance micro-encapsulated probiotics Bifidobacterium longum Rosell®-175, that are highly stable and resistant to gastric acidity, compression and heat shock. This probiotic has been associated with numerous health benefits, such as normalising gastrointestinal transit, inhibiting the growth of harmful bacteria, boosting the immune system, and effectively reducing stress induced gastrointestinal symptoms. This probiotic has also been shown to improve gut and cognitive health via the gut-brain axis., enhancing mood and reducing stress related symptoms.
Liposomal Vitamin C
Liposomal Vitamin C is encapsulated in a lipid bilayer, allowing 233% greater absorption and retention than standard Vitamin C. This form offers superior antioxidant protection, helps defend the lens against UV damage, reduces cataract risk, and boosts immune function, with studies indicating enhanced neuron growth, immune support, and ocular health benefits.
Liposomal Vitamin C
Liposomal Vitamin C is encapsulated in a lipid bilayer, allowing 233% greater absorption and retention than standard Vitamin C. This form offers superior antioxidant protection, helps defend the lens against UV damage, reduces cataract risk, and boosts immune function, with studies indicating enhanced neuron growth, immune support, and ocular health benefits.

Eye Fatigue
BILBERON®-25 Bilberry Extract effectively reduces eye fatigue by enhancing blood flow, protecting retinal cells, reducing oxidative stress, and aiding muscle recovery. A clinical study conducted among healthy 22 healthy adults treated with 120mg daily showed improvement in eye fatigue (31%) and eye dryness (45%).

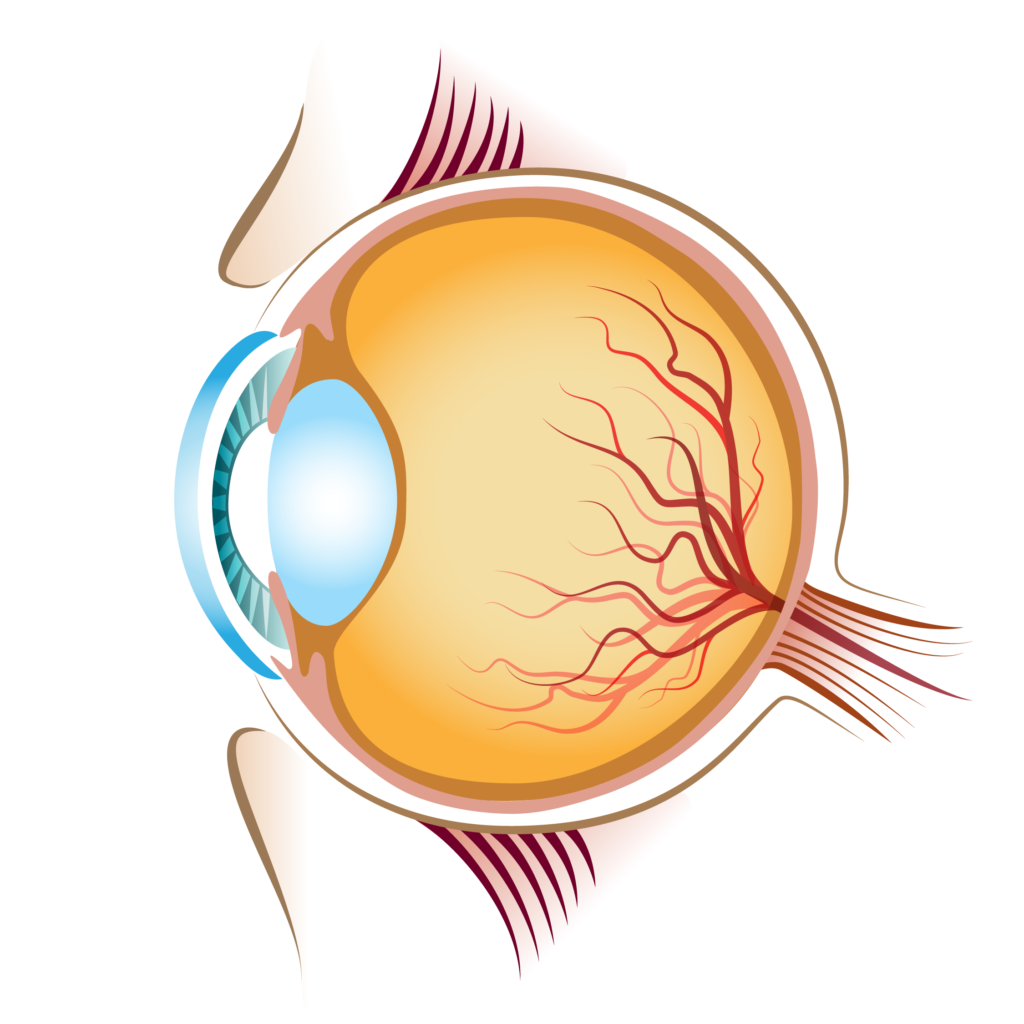

Macular Pigment Optical Density (MPOD) by
XanMax® increases MPOD (Macular Pigment Optical Density) by delivering lutein and zeaxanthin, the primary carotenoids in the macula. MPOD protects the retina by filtering harmful blue light, neutralizing oxidative stress, and enhancing visual performance. A clinical study involving 60 elderly volunteers showed a 40% improvement in MPOD after 180 days. This is especially beneficial for those exposed to prolonged screen time, blue light, or age-related vision decline.
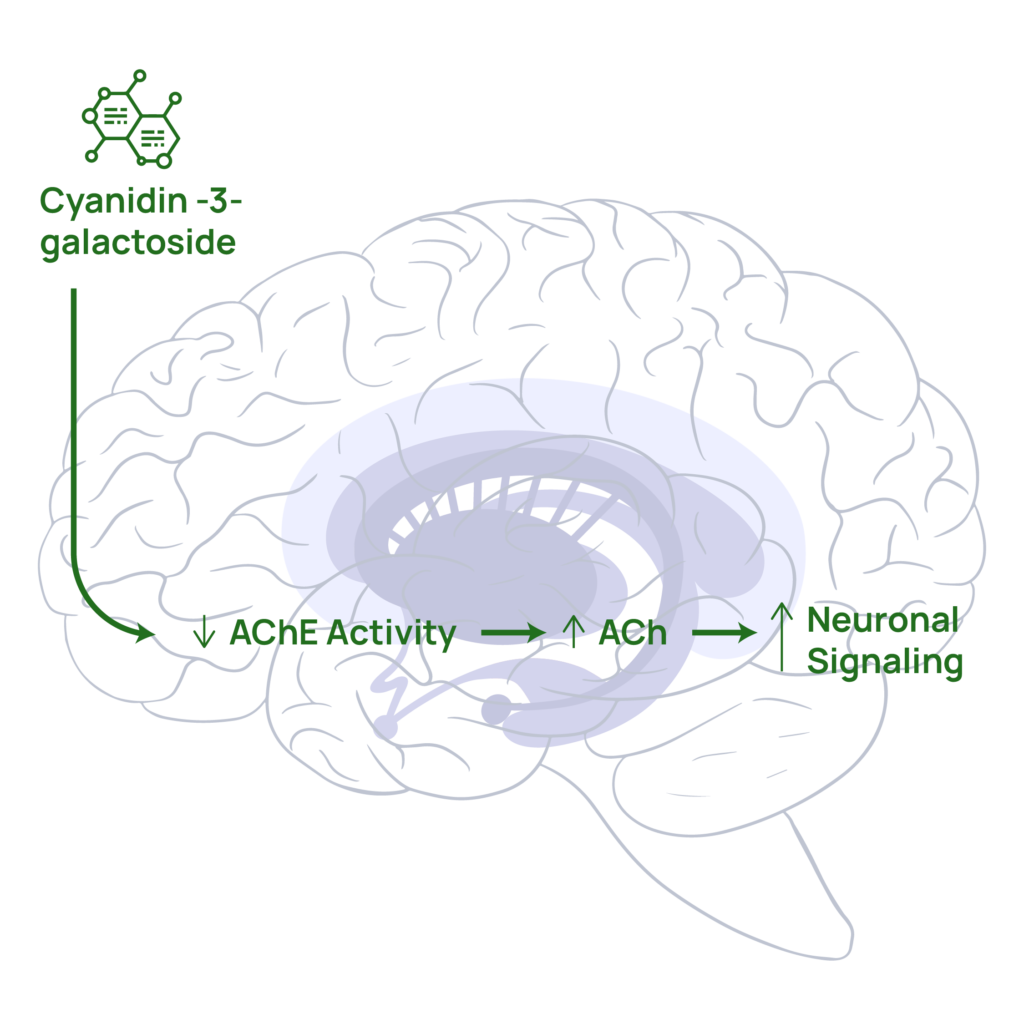
1. BRAINBERRY®’s hero compound, Cyanidin-3 galactoside crosses the blood-brain barrier, enhancing brain perfusion and oxygen uptake.
2. Enhances neural signaling, leading to faster and more accurate visual processing and task performance, improving eye-hand coordination.
3. Maintains an optimal level of Brain Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF), an essential protein for brain health involved in neuronal plasticity and neuroprotection mechanisms that improve learning and memory.

Who is LACTOEYE® with BRAINBERRY® For?
LACTOEYE® with BRAINBERRY® is ideal for individuals looking to improve vision, reduce eye strain, and enhance cognitive function. Perfect for those experiencing digital eye fatigue, memory challenges, or general mental fog, it supports eye health, mental clarity, and immunity. Suitable for students, professionals, night drivers and older adults, LACTOEYE® with Brainberry® helps you stay sharp, focused, and comfortable throughout the day.
Professionals
Students
Athletes
Night driver
Contact lens wearers
Gamers or streamers
Suitable for all age group
Professionals
Students
Athletes
Night driver
Contact lens wearers
Gamers or streamers
Suitable for all age group

THINK As BRIGHT As You SEE

Filters blue light & relieves eye strain

Improves eyesight & visual clarity

Enhances cognitive performance

Improves immune system

Antioxidant protection

Promotes digestive health

Clinically Proven Results
Clinically Proven Results
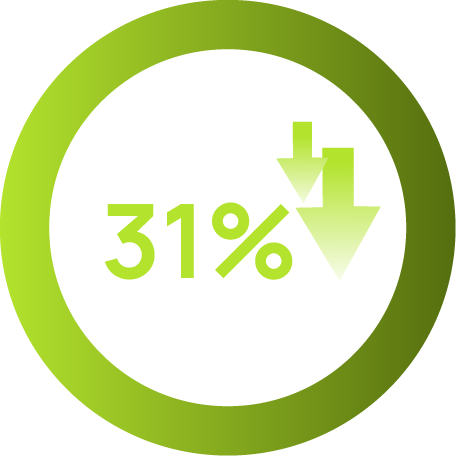

eye-fatigue
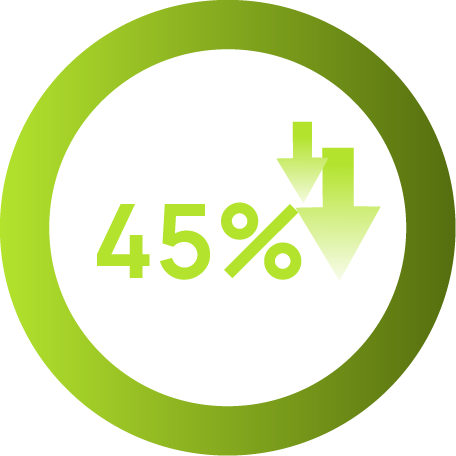

eye-dryness
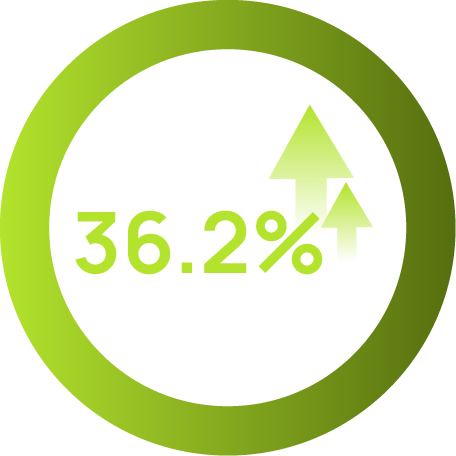

focus & concentration

reaction time

macular pigment optical density (MPOD)
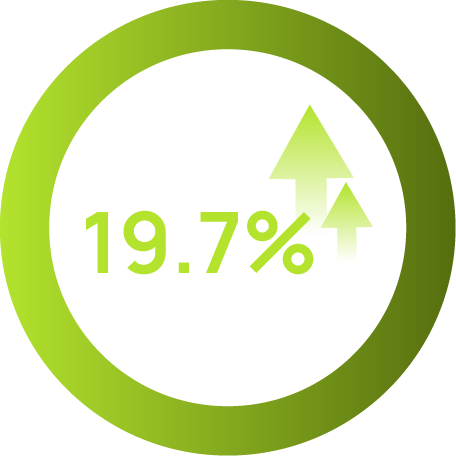

eye-hand coordination

billion CFU probiotics

eye-fatigue

eye-dryness

focus & concentration

reaction time

macular pigment optical density (MPOD)

eye-hand coordination

billion CFU probiotics

Why Choose LACTOEYE® with BRAINBERRY®?
LACTOEYE® with BRAINBERRY® is an advanced, multi-benefit formula designed to support eye health, boost cognitive performance, and strengthen immunity. Packed with clinically proven ingredients like Bilberon® Bilberry Extract, Brainberry® Aronia Berry Extract, and XanMax® Marigold Flower Extract, it provides comprehensive vision protection, enhances mental clarity, and promotes overall wellness.

For All Ages
LACTOEYE® with Brainberry® is safe and effective for people of all ages, starting from as young as 3 years old. This makes it a versatile supplement that can support the health of children, adults, and seniors alike. Share the delicious berry dose with your beloved family members and friends from today.

Cost-Saving
LACTOEYE® with Brainberry® provides great value by addressing multiple health areas. It supports not just eye health, but also brain function, gut health, and immune system support. With one product, you can boost multiple aspects of your well-being, making it a more affordable option compared to buying separate supplements for each of these areas.

Take It Wherever & Whenever
The small, portable sachets of LACTOEYE® with Brainberry® make it incredibly easy to take with you wherever you go. Whether at home, at work, or traveling, you can enjoy the benefits of LACTOEYE® with Brainberry®anytime and anywhere, without any hassle.

Got Questions?
We’ve Got Answers
LACTOEYE® with BRAINBERRY® is an advanced supplement that supports eye health, cognitive function, digestive health and immune wellness. It contains powerful ingredients like Bilberon® Bilberry Extract, Brainberry® Aronia Berry Extract, XanMax® Marigold Flower Extract, micro-encapsulated probiotics and Liposomal Vitamin C to help relieve eye strain, boost mental clarity, and strengthen immunity.
Bilberon® Bilberry Extract and XanMax® Marigold Flower Extract in LACTOEYE® with BRAINBERRY® reduce eye dryness and strain by supporting hydration and filtering blue light, helping to relieve symptoms caused by prolonged screen time.
Yes, Brainberry® Aronia Berry Extract in LACTOEYE® with BRAINBERRY® is clinically proven to enhance brain function by improving memory, focus, and overall cognitive health. It works by increasing neural signaling and supporting optimal brain oxygenation.
Liposomal Vitamin C and micro-encapsulated probiotics in LACTOEYE® with BRAINBERRY® boost immune health by providing antioxidant support, promoting gut health, and enhancing the body’s natural defenses against oxidative stress.
LACTOEYE® with BRAINBERRY® is suitable for all ages from kids of 4 years old looking to relieve eye strain, improve mental clarity, and strengthen immunity. It’s ideal for students, professionals, and older adults who spend a lot of time on digital devices.
Take 1 sachet daily, direct consume, for optimal benefits. This dosage provides daily support for eye health, cognitive function, and immunity.
Many users experience reduced eye strain and improved hydration within 1-2 months. Enhanced cognitive clarity and immunity benefits may also become noticeable with consistent daily use.
LACTOEYE® with BRAINBERRY® is made from natural, clinically tested ingredients and is generally safe for daily use. However, if you have any specific allergies or medical conditions, consult your healthcare provider before use.
| Weight | N/A |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | N/A |
| LACTOEYE® with BRAINBERRY® | 2 Units Rebate RM 11, Lactoeye Brainberry 21's, Lactoeye Brainberry Buy 6 Free 1 |





Reviews
There are no reviews yet.